Focos
Arquitecto, arquitecto de campos de golf, urbanista, arquitecto paisajista, urbanista paisajista, urbanista de parques, urbanista, arquitecto paisajista profesional (PLA), consultor paisajista, diseñador de jardines, diseñador de espacios exteriores, gestor de proyectos paisajistas, urbanista, diseñador urbano, diseñador de parques, artista paisajista.
Los paisajistas y arquitectos paisajistas utilizan plantas, árboles y elementos artificiales, como fuentes y luminarias, para dar vida a los espacios exteriores.
Estos profesionales del paisajismo transforman parques, jardines, espacios públicos, campus universitarios y corporativos, parques médicos y jardines domésticos en espacios hermosos y ecológicos que promueven el bienestar y la tranquilidad. ¡Literalmente ayudan a dar forma a nuestra experiencia del aire libre!
Para lograrlo, combinan la creatividad con la ciencia, trabajando en estrecha colaboración con arquitectos y urbanistas para garantizar que cada proyecto sea sostenible y visualmente atractivo. Todo se planifica hasta el último detalle, desde el drenaje y las condiciones del suelo hasta las zonas de descanso y la selección de plantas, creando espacios que conectan a las personas con la naturaleza al tiempo que resuelven los retos medioambientales.
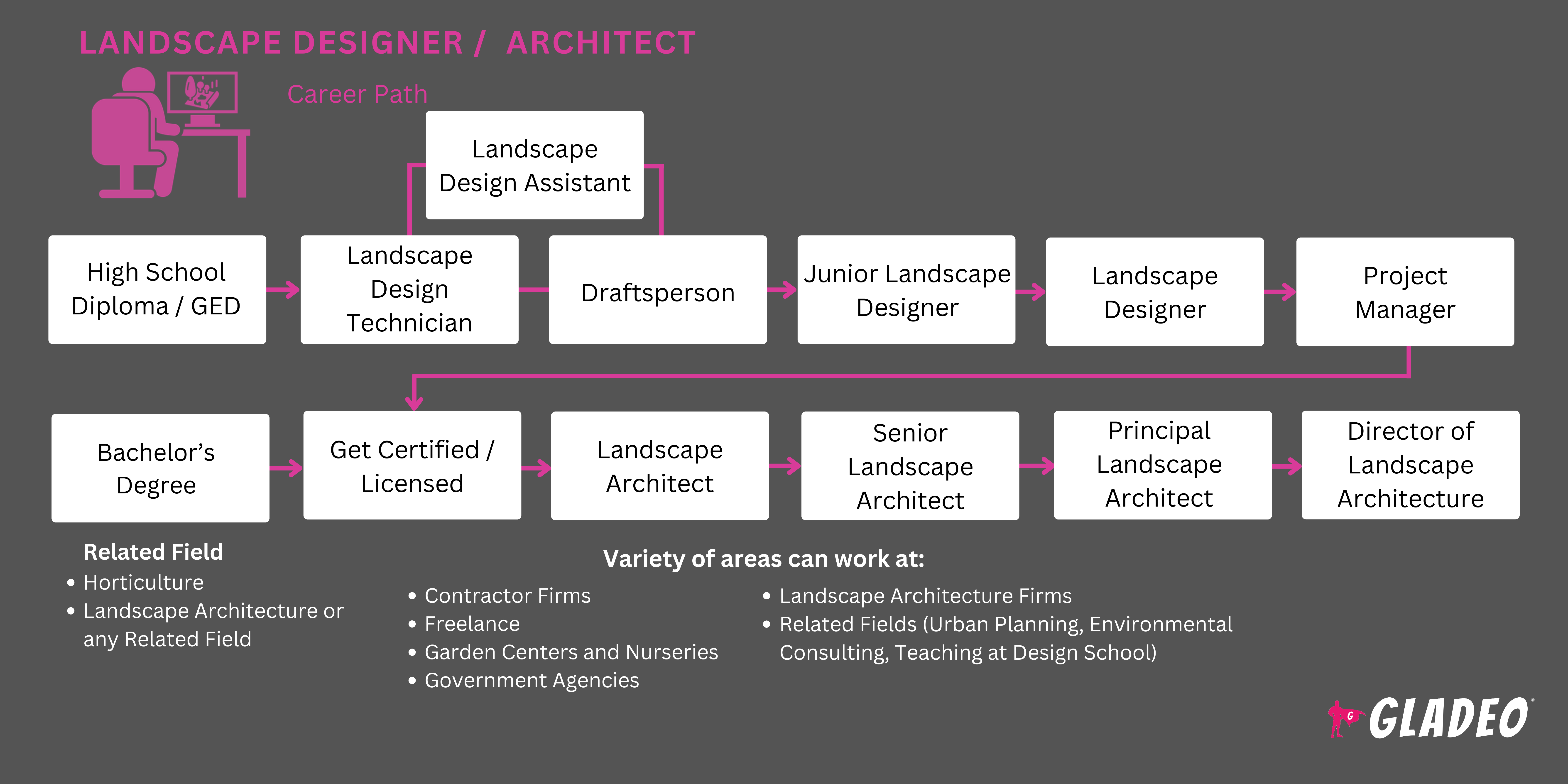
Las diferencias clave entre los diseñadores paisajistas y los arquitectos paisajistas son sus cualificaciones, el alcance de los proyectos y sus áreas de especialización. Por ejemplo, los arquitectos paisajistas suelen tener un título universitario y una licencia, lo que les permite gestionar proyectos a gran escala que implican una planificación compleja del emplazamiento, evaluaciones de impacto ambiental y colaboración con ingenieros.
Los diseñadores paisajistas se centran en proyectos residenciales más pequeños y, por lo general, no necesitan tener un título universitario ni una licencia. Su trabajo se centra en la selección estética de las plantas y el diseño de la distribución, embelleciendo los espacios sin el enfoque estructural que requieren los proyectos de mayor envergadura.
- Transformar los espacios exteriores en zonas bonitas y funcionales.
- Contribuir a la sostenibilidad medioambiental
- Trabajar al aire libre con la naturaleza
- Mantener las plantas, los arbustos y los árboles sanos y protegidos contra las plagas.
- Ejercicio físico diario
- Colaborar con una variedad de profesionales en diferentes campos.
Horario de trabajo
Los diseñadores paisajistas y los arquitectos paisajistas suelen trabajar a tiempo completo, con posibilidad de horas extras en algunos casos. Dividen su tiempo entre oficinas y emplazamientos al aire libre, coordinándose con clientes, contratistas y otras partes interesadas.
Funciones típicas
Tenga en cuenta que las funciones varían dependiendo de si se trata de un diseñador paisajista o un arquitecto paisajista.
- Reúnete con los clientes para revisar sus ideas, los requisitos del proyecto, los plazos y los presupuestos.
- Visite los sitios propuestos para evaluar las características del terreno, las condiciones del suelo y otros factores ambientales, como las precipitaciones previstas.
- Utilizar sistemas de información geográfica para recopilar y analizar datos geográficos del emplazamiento.
- Analizar informes medioambientales para abordar cuestiones como el drenaje, el control de la erosión y el uso de la energía.
- Desarrollar conceptos y bocetos de diseño. Integrar elementos naturales del terreno, como árboles y fuentes de agua, en los diseños. Revisar los diseños con los clientes.
- Incorporar los comentarios de los clientes y crear planos detallados del sitio, con especificaciones y estimaciones de costes.
- Utilizar software de diseño y dibujo asistido por ordenador para preparar representaciones gráficas.
- Elija materiales sostenibles y plantas compatibles con el clima y el suelo del lugar.
- Planifique la conservación del agua incorporando plantas resistentes a la sequía y un riego eficiente.
- Incorporar elementos de infraestructura ecológica, como tejados verdes y jardines pluviales o sistemas de recogida de agua de lluvia y aguas grises.
- Desarrollar estrategias de gestión de aguas pluviales para prevenir la erosión.
- Diseñar distribuciones para pasillos, zonas de descanso e iluminación con el fin de mejorar la accesibilidad y la estética.
- Coordinar con estimadores de costes, arquitectos, ingenieros, personal de construcción y subcontratistas, según sea necesario.
- Presentar las propuestas de diseño definitivas a los clientes, organismos gubernamentales o partes interesadas de la comunidad para su aprobación.
- Gestionar los plazos y la calidad de los proyectos. Visitar las obras mientras se está trabajando. Revisar los materiales, las normas de construcción y el cumplimiento de los planos.
Obligaciones adicionales
- Realizar consultas de seguimiento con los clientes.
- Prepare representaciones visuales para ilustrar el crecimiento previsto del paisaje.
- Crea planes de plantación estacionales.
- Manténgase al día con las tendencias de diseño, la tecnología y las prácticas sostenibles.
- Planificar la restauración del paisaje natural (por ejemplo, humedales).
- Desarrollar estrategias de marketing para publicitar los servicios.
Habilidades sociales
- Atención al detalle
- Colaboración
- Comunicación
- Creatividad
- Orientado al servicio al cliente
- Observador
- Paciente
- Resolución de problemas
- Orientado a la seguridad
- Gran capacidad de escucha
- Trabajo en equipo
- Gestión del tiempo
Habilidades técnicas
- Los diseñadores y arquitectos paisajistas deben estar familiarizados con lo siguiente:
- Software de modelado 3D (por ejemplo, SketchUp, Rhino)
- Software de diseño (por ejemplo, AutoCAD, GIS)
- Métodos y materiales de construcción
- Estimación de costes y elaboración de presupuestos
- Técnicas de topografía y medición de terrenos
- Dibujo técnico y delineación
- Gestión de proyectos
- Normas de seguridad estatales y locales
- Normativa medioambiental y urbanística
- Sistemas de riego y alumbrado
- Estrategias de control de la erosión
- Horticultura y cuidado de las plantas
- Ciencia del suelo y sistemas de drenaje
- Sistemas de riego y gestión del agua
- Planificación de la adaptación al clima y la resiliencia
- Prácticas paisajísticas sostenibles
- Pesticidas y fertilizantes
- Ecología del paisaje y biodiversidad
- Empresas de arquitectura paisajística
- Empresas de construcción e ingeniería
- Organismos gubernamentales (por ejemplo, departamentos de urbanismo, parques y ocio, bases militares)
- Promotores inmobiliarios
- Organizaciones medioambientales
- Centros comerciales y locales comerciales
- Sede central de la empresa
- Instalaciones médicas
- Universidades y facultades
Los diseñadores y arquitectos paisajistas deben combinar la creatividad con la funcionalidad para crear diseños que sean visualmente atractivos, prácticos y sostenibles. Esto requiere mucha capacidad para resolver problemas y flexibilidad, ya que deben sopesar factores como las limitaciones presupuestarias, el impacto medioambiental y los requisitos normativos.
Además, no siempre es fácil satisfacer las demandas de los clientes dentro del presupuesto y los plazos deseados. Cuando los proyectos se retrasan o los costes superan el presupuesto, ¡la tensión puede aumentar! Por eso es esencial mantener una comunicación abierta y continua.
Los trabajadores de este campo pasan mucho tiempo al aire libre, visitando obras, supervisando los avances y garantizando el cumplimiento de los planes de diseño. Esto requiere resistencia, así como compromiso con el control de calidad y capacidad para trabajar con otras personas con el fin de alcanzar objetivos comunes.
Desde paisajes residenciales hasta proyectos comerciales e industriales, el mundo del diseño paisajístico y la arquitectura se centra cada vez más en la sostenibilidad, la resiliencia y la integración tecnológica. De hecho, el impulso hacia la sostenibilidad nunca ha sido tan fuerte, con un énfasis creciente en infraestructuras ecológicas, como jardines de lluvia y biofiltros ecológicos, el uso de plantas autóctonas, tejados verdes, paisajes permeables y muros vivos que gestionan las aguas pluviales, reducen la contaminación y refrescan las zonas urbanas.
En términos de resiliencia, las estrategias de diseño resiliente abordan retos climáticos como las inundaciones y el calor extremo, incorporando plantas adaptables y técnicas de mitigación de desastres naturales.
Mientras tanto, herramientas avanzadas como el modelado 3D y los sistemas de información geográfica están mejorando la precisión y la eficiencia en la planificación, mientras que la cartografía con drones y la realidad virtual facilitan la visualización de los proyectos y la evaluación de los emplazamientos.
Muchos arquitectos paisajistas se interesaron desde muy temprana edad por el arte, el diseño, la naturaleza, las plantas y la jardinería. Es posible que sintieran curiosidad por la ecología, la biología o los estudios medioambientales, lo que les permitió comprender cómo funcionan los sistemas naturales.
- Los paisajistas deben tener, como mínimo, un título de secundaria o GED. Las clases de diseño, horticultura y jardinería en centros de formación profesional pueden resultar útiles.
- Por lo general, no necesitan ningún tipo de certificación o licencia.
- Los arquitectos paisajistas deben tener, como mínimo, una licenciatura en Arquitectura Paisajista o una licenciatura en Ciencias en Arquitectura Paisajista de un programa aprobado por la Junta de Acreditación de Arquitectura Paisajista. Aproximadamente el 18 % de ellos tiene un máster.
- Todos los estados exigen que los arquitectos paisajistas cuenten con una licencia. En primer lugar, deben aprobar el Examen de Registro de Arquitectos Paisajistas (LARE), gestionado por el Consejo de Juntas de Registro de Arquitectos Paisajistas. Los requisitos para presentarse al examen varían según el estado.
- El examen abarca temas como:
■ Inventario, análisis y gestión de proyectos
■ Planificación y diseño
■ Documentación y administración de la construcción
■ Nivelación, drenaje y gestión de aguas pluviales
- Algunos estados exigen pruebas adicionales además del LARE.
- Las certificaciones opcionales incluyen:
- Asociación de Administradores de Instalaciones Físicas - Profesionales de Instalaciones Educativas
- Asociación de Diseñadores Paisajistas Profesionales - Diseñador Paisajista Profesional Certificado
- Asociación de Administradores Estatales de Llanuras Aluviales - Administrador Certificado de Llanuras Aluviales
- Congreso para el Nuevo Urbanismo - Programa de acreditación CNU
- Instituto de Especificaciones de Construcción - Especificador de Construcción Certificado
- Instituto de Diseño y Construcción de Estados Unidos - Certificación profesional designada en diseño y construcción
- Agencia de Protección Ambiental - Paisajista cualificado en eficiencia hídrica
- Instituto de Certificación GIS - Profesional en Sistemas de Información Geográfica
- Asociación Americana de Constructores de Campos de Golf - Constructor de campos de golf certificado
- Techos verdes para ciudades saludables - Profesional en techos verdes
- Instituto para la Infraestructura Sostenible - Profesional de la Sostenibilidad Envision
- EnviroCert: profesional certificado en control de la erosión y los sedimentos y certificación nacional de infraestructura ecológica.
- Instituto Internacional Living Future - Acreditación Living Future
- Sociedad Internacional de Arboricultura - Credenciales de arbolista certificado
- Gestión de plantas invasoras - Gestor certificado de plantas invasoras
- Asociación de Riego - Diseñador de Riego Certificado - Paisajismo
- Asociación Nacional de Profesionales del Paisajismo - Técnico Certificado en Paisajismo
- Instituto Nacional de Prevención del Delito - Prevención del delito mediante el diseño ambiental Designación profesional
- Asociación Nacional de Recreación y Parques - Profesional certificado en parques y recreación
- Centro Nacional de Aguas Pluviales - Inspector certificado de aguas pluviales
- Asociación de Agricultura Orgánica del Noreste - Profesional acreditado en cuidado orgánico de la tierra
- Instituto de Gestión de Proyectos - Profesional en Gestión de Proyectos
- Sociedad para la Restauración Ecológica - Profesional Certificado en Restauración Ecológica
- Sociedad Americana de Ciencias del Suelo - Científico profesional certificado en ciencias del suelo
- Iniciativa de Sitios Sostenibles - Profesional acreditado por SITES
- El Centro para el Diseño Sanitario: acreditación y certificación del diseño basado en la evidencia.
- Consejo de Construcción Ecológica de EE. UU. - Profesional acreditado por LEED
- Academia Mundial de Parques - Profesional certificado en parques
- Los programas de arquitectura paisajística deben estar acreditados por la Junta de Acreditación de Arquitectura Paisajística.
- Busca programas que ofrezcan experiencia práctica y cuenten con instalaciones y herramientas modernas.
- Ten en cuenta el costo de la matrícula, los descuentos y las oportunidades de becas locales (además de la ayuda federal).
- Revisar las tasas de graduación y las estadísticas de inserción laboral tras la graduación.
- Piensa en tu horario y flexibilidad a la hora de decidir si matricularte en un programa presencial, online o híbrido. Es probable que algunas clases deban realizarse de forma presencial para adquirir experiencia práctica en el mundo real.
- Toma cursos de arte, biología, ciencias ambientales, ciencias de la Tierra, química y física; las clases de nivel avanzado también son beneficiosas.
- Adquiera experiencia mediante prácticas o trabajos a tiempo parcial en empresas de paisajismo, diseño u organizaciones medioambientales.
- Desarrolla habilidades en dibujo, software de diseño y sistemas de información geográfica.
- Participa en clubes medioambientales, de sostenibilidad y de geología.
- Crea un portafolio que muestre proyectos de diseño, trabajo de campo, mapeo y análisis de datos.
- Participa en ferias científicas, proyectos en equipo y actividades de liderazgo para mejorar tus habilidades de trabajo en equipo y gestión de proyectos.
- Manténgase al día sobre las nuevas herramientas, el software y las tendencias leyendo publicaciones del sector, como Landscape Journal, y viendo vídeos educativos.
- Solicita una entrevista informativa con un profesional en activo. ¡Pasar un día observando su trabajo también es una forma estupenda de aprender!
- Empieza a crear una red de contactos asistiendo a eventos del sector, participando en foros online y afiliándote a organizaciones profesionales como la Sociedad Americana de Arquitectos Paisajistas.
- Mantén el contacto con profesores, mentores y compañeros que puedan servirte de referencia y ofrecerte orientación profesional.
- Utiliza el centro de orientación profesional de tu escuela para obtener ayuda con tu currículum y apoyo en la búsqueda de empleo.
- Pregunte a los profesionales del paisajismo de su red sobre las ofertas de empleo.
- Echa un vistazo a portales de empleo como Indeed.com, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, Monster, CareerBuilder, SimplyHired, ZipRecruiter, USAJOBS y las páginas web de empresas locales.
- Si no tienes suficiente experiencia, busca prácticas, aprendizajes o puestos de nivel inicial en empresas de diseño paisajístico y arquitectura.
- Prepara un currículum y un portafolio sólidos que destaquen tus proyectos de diseño, tus habilidades con el software y cualquier experiencia práctica. Fíjate en las palabras clave utilizadas en las ofertas de empleo, como por ejemplo:
- Evaluaciones medioambientales
- Mapeo de campo
- Sistemas de Información Geográfica
- Selección de plantas y conocimientos de horticultura
- Análisis del sitio
- Diseño sostenible
- Planificación urbana
- Consulte ejemplos de currículums e incorpore palabras clave aplicables en el suyo.
- Repase las preguntas habituales de las entrevistas para estar preparado. Entre las preguntas tipo que pueden plantearse en una entrevista se incluyen:«¿Cómo aborda el equilibrio entre el atractivo estético y la sostenibilidad medioambiental en un proyecto de diseño paisajístico?» o «Describa una ocasión en la que se enfrentó a unas condiciones difíciles en el emplazamiento. ¿Cómo adaptó su diseño para solucionarlo?».
- Practica entrevistas simuladas para ganar confianza. Muestra un entusiasmo genuino por la arquitectura paisajística y cualquier área en la que quieras especializarte, como el diseño sostenible o la planificación urbana.
- Vístete adecuadamente para las entrevistas.
- Pide consejo a tu supervisor sobre la planificación de tu carrera profesional. Hazle saber que estás interesado en ascender y que estás dispuesto a abordar proyectos cada vez más complejos.
- Si eres diseñador paisajista y no tienes una licenciatura, obtén una licenciatura en arquitectura paisajística o una licenciatura en ciencias en arquitectura paisajística y obtén la licencia.
- Si eres arquitecto paisajista con una licenciatura, haz un máster en arquitectura paisajista.
- Realice cursos de formación continua y obtenga una certificación avanzada, como la de profesional acreditado por SITES o profesional acreditado por LEED.
- Establecer relaciones sólidas con los organismos reguladores.
- Busca la orientación de profesionales con experiencia en paisajismo. Orienta a los diseñadores noveles, compartiendo conocimientos y consejos.
- Manténgase al día sobre las herramientas y la tecnología del sector, dominando programas como AutoCAD, ArcGIS y Adobe Creative Suite.
- Únete a organizaciones profesionales, publica artículos, da charlas en conferencias y participa en eventos del sector.
- Manténgase al tanto de las oportunidades laborales internas y esté atento a las vacantes externas, si es necesario para ascender.
- Considera la posibilidad de trasladarte a zonas con una gran demanda de diseñadores paisajistas y arquitectos, como Nueva York, California, Florida, Texas, Pensilvania, Connecticut, Maryland y Colorado.
Sitios web
- Instituto Americano de Planificadores Certificados
- Asociación Americana de Planificación
- Sociedad Americana de Arquitectos Paisajistas
- ArchDaily
- Asociación de Administradores de Instalaciones Físicas
- Asociación de Diseñadores Paisajistas Profesionales
- Asociación de Administradores Estatales de Llanuras Aluviales
- Congreso para el Nuevo Urbanismo
- Instituto de Especificaciones de Construcción
- Consejo de Educadores en Arquitectura Paisajística
- Consejo de Juntas de Registro de Arquitectos Paisajistas
- Instituto de Diseño y Construcción de Estados Unidos
- EcoBuilding Pulse
- EnviroCert
- Asociación de Investigación en Diseño Ambiental
- Agencia de Protección Ambiental
- Instituto de Certificación GIS
- Asociación Americana de Constructores de Campos de Golf
- Techos verdes
- Techos verdes para ciudades saludables
- Instituto para la Infraestructura Sostenible
- Sociedad Internacional de Arboricultura
- Centro Nacional de Información sobre Especies Invasoras
- Asociación de Riego
- Land8
- Fundación de Arquitectura Paisajística
- Revista del contratista paisajista
- Diario paisajístico
- Futuro vivo
- Asociación Nacional de Profesionales del Paisajismo
- Asociación Nacional de Recreación y Parques
- Centro Nacional de Aguas Pluviales
- Asociación de Agricultura Ecológica del Noreste
- Planetizen
- Instituto de Gestión de Proyectos
- Sociedad para la Restauración Ecológica
- Sociedad Americana de Ciencias del Suelo
- Iniciativa de Sitios Sostenibles
- El Centro para el Diseño Sanitario
- La Fundación del Paisaje Cultural
- Consejo de Construcción Ecológica de Estados Unidos
- Instituto de Suelo Urbano
- USGBC
- Arquitectura paisajística mundial
- Academia Mundial de Parques
Libros
- Diseñar con plantas, por Piet Oudolf
- Normas gráficas de arquitectura paisajística, por Leonard J. Hopper
- Normas para ahorrar tiempo en arquitectura paisajística, por Charles W. Harris
Los diseñadores y arquitectos paisajistas desempeñan un papel crucial en la creación y el mantenimiento de espacios exteriores hermosos, funcionales y sostenibles. Pero para aquellos que quieran considerar otras opciones profesionales, ¡echad un vistazo a las alternativas que se indican a continuación!
- Arquitecto
- Dibujante arquitectónico y civil
- Botánico
- Ingeniero civil
- Técnico y técnico superior en ingeniería civil
- Gerente de construcción
- Redactor
- Planificador de restauración medioambiental
- Científico medioambiental
- Floristería
- Horticultor
- Hidrólogo
- Diseñador de interiores
- Técnico de guardería
- Técnico en topografía y cartografía
- Topógrafo
- Especialista en sostenibilidad
- Urbanista
Fuente de noticias
Empleos destacados

Cursos y herramientas en línea

Expectativas salariales anuales
Los nuevos trabajadores comienzan con un salario de alrededor de 61 000 dólares. El salario medio es de 79 000 dólares al año. Los trabajadores con mucha experiencia pueden ganar alrededor de 97 000 dólares.





